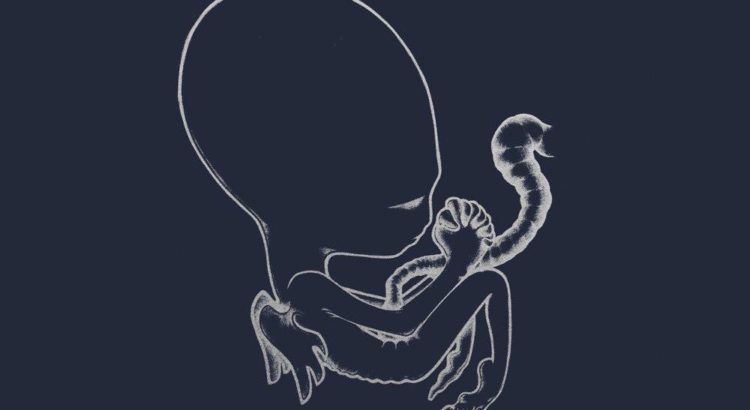
Author: Roberto Terracciano

Hooked Up By Design. Public Space and Interface Politics in Grindr
We crossed our paths at the huge demonstration against male violence on women in Rome: he had bushy eyebrows shadowing a secant gaze, his beard was short and whirled softly upon his cheeks, his canvas shopper swinging rhythmically and his t-shirt fell down his shoulders like from a hanger. I had seen him elsewhere, his profile-pic showing up on my ‘people-you-might-know’ frame on Facebook. One evening, a few days days later, just before parking my head upon my pillow, I was tired of my Grindrography and started playing with the “tribes” filter, one the few available in the free version. Then I toggled otters.

In my understanding, otters are like bears but skinnier; it is all that I know, I don’t know if there is a subculture sustaining that kind of body, if we are talking about bodies. The first one is at 180 km. I have learnt to guess locations by numbers: 200 meters is the Holiday Inn I see from my balcony, 3 km is downtown, 400 km is Florence, 700 Turin, 1600 London, 2000 Lisbon. 180 km is Rome. There he smirked and frowned in a sort of fake embarrassment in the very first cell next to mine. “Hi there, I think I saw you at the rally but I didn’t stop you because I’m not really good at this, do you fancy chatting a bit?”
A different geography exists on hook up apps, and it is designed by the coordinates of each device – connecting to the desires (and boredom) of a body caught in parameters such as height, weight, age, tribe and a reason to stay online. Right now? Sex? Friendship? Chat? Date? Relationship? Nope. Boredom is not encoded in this kind of geography. It is a viscous geography, thicker in big cities, wherein the free version doesn’t let you see beyond a couple of blocks, and more rarefied in peripheries and countryside where the first person online is within one hour ride. It is a layered geography wherein people walking in the same square meter cannot see each other because they plane on different strata, vertically bordered by the properties defining their identity and desires.
Despite being as old as a 2-grader, not only Grindr has revolutionized gay sociality but it is already a solid technocultural reference in novels, movies, series and artistic installations. Launched in 2009 by its current CEO, Joel Simkhai, the grid designed app has somehow passed the coolness test for online chats. In fact, they are no longer perceived as risky or designed for people who cannot handle offline sociality. Apps opened new spaces for interaction between the digital and physical worlds, each app installed on a user’s phone being a subjectivity module in a spatiality which is neither completely public, neither completely private. After being cited by Stephen Fry on BBC’s Top Gear, Grindr’s download-count rose exponentially as did concerns about privacy, triangulation and trackability.
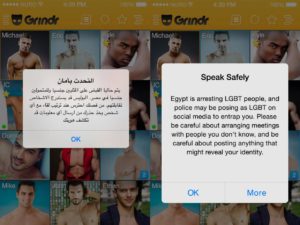
Art in the times of Grindr
In 2014, Dutch artist Dries Verhoeven caused a scandal over the relationship between Grindr, the art market and the kind of spatiality produced by the app with his installation Wanna Play? Liebe in Zeiter von Grindr – Love (sic) at the time of Grindr. The residency, commissioned by Berlin artistic space Hebbel am Ufer (HAU) and by the Dutch government, consisted in a container reproducing and mixing up Berlin’s physical space with the digital one: the fourth wall was made of glass allowing passers-by to look inside. The grids, the profiles and the chats from Verhoeven’s app were projected onto the back wall in negative, in a goofy attempt to protect privacy. Instead, the installation was perceived as an open attack to the communities in Kreuzberg, a neighborhood historically inhabited by migrant (and) LGBTQI people. One user, Parker Tilghman, after having figured out that his chat session was publicly shown, punched Verhoeven and called him “a digital rapist” on Facebook. In an angry yet lucid post, published one week later in Mute Magazine, Jacob Rosemberg dismantled Verhoeven’s conceptual container (and the attempt on HAU’s behalf to extract value from the accident, mending the wounds produced in Kreuzberg with the thread of relational art). The post disassembled Verhoeven’s belief that he was really contributing to a debate on public and private spaces, by noting that public and private spheres – and the the difference between the two – are deeply embedded in a context governed by private interests.
A different note is struck by Andrés Jaques’s installation Intimate Strangers, produced by his studio of critical architecture Office for Political Innovation, and part of the exhibition “Fear and Love” showcased at the Design Museum in London until April 2017. Exposed on several screens of different sizes and shapes and divided in 4 episodes, Intimate Strangers opens up to contradictions in the design of Grindr and of other proximity-based people discovery apps, by analyzing the way in which they capture the users’ subjectivity and by looking closely at the lines of flight that it emits. In the four episodes, the Spanish American architect describes hook up apps as a technology for a transmedia urbanism, spreading in big cities and reflecting the burgeoning gentrification process of former queer neighborhoods, that were turned in “a new mainstream”. But it also explores the way in which the technology upon which Grindr is based is a backdoor for control (in states with institutionalized homophobia) and a technological tool for resistance allowing for the formation of solidary networks. The show was also advertised on Grindr’s social accounts. But whereas Simkhai blog on Grindr’s corporate site and Grindr’s Instagram narrates an open app, sensitive to trans rights and non-indentitary politics, the User experience design (UX Design) of the application tells a completely different story.
Digital public space and subjectivation
In his autoethnography on bareback (both as a practice and as a subculture), Tim Dean draws a genealogy of the logic behind the privatization and the securitization of spaces otherwise open. The cruising space where bodies me(e)t emerged in anonymous forms of encounters and expressed the excess of legitimized familiar intimacy, soldering forms of solidarity between sexual partners. Quite ironically, Dean’s Unlimited Intimacies was published in the same year Simkhai launched his app. But in 2009, dating online was anything but a new story. Among other things, Dean documents how the darkness of an open space at night or the dim-light of a darkroom, became misty in saunas and started to shine through the sleek and clean design of computers. This illumination marks a securitization of the risk of encounters, but that does not mean that it creates a safe space for encounters.
Hook up apps dragged the cruising space out of its dark limits and redistributed it onto the urban space, in the private perimeters of houses, gyms, clubs – fragmenting a sociality of data-subjects who un-see each other on the basis of the desire captured by the app. As in the dystopian novel by China Miéville, The City and The City, apps produce multilayered spatialities in which citizenship (in the case of the novel) and identification with a tribe (in Grindr) directs sociality on rails nailed to the same ground but never touching. The selective vision is a very peculiar bordering device in the interfaces of this kind of apps and it governs the sociality between its users.
According to the visual culture scholar Benjamin Bratton, software is a form of sovereignty distributed on a vertical but not hierarchical geography. That is, it is not delimited by geographical borders but it is designed by “accidental megastructures” made of users, cities, interfaces the cloud and, of course, platforms. The interfaces of platforms, returning a new vision of the world, respond to a problematic software architecture as they put to work the bodies transiting on the app, producing a narration that strips those bodies of their own data: the platforms and their interfaces design a society in their own likeness.
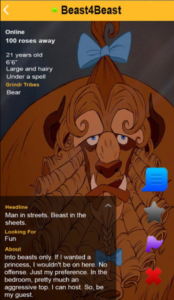
The narration of the quantified self accompanies the recodifications of disruptive cultures into secured identities. For instance, bears’ counterculture initially broke down the dominant gay male aesthetics, and later reaffirmed the model of a hegemonic masculinity, often a white one (m4m, no fat, no fems, no Asians, no blacks). In a space where geographic positions define an aspect of a user, that is a property, the quantified self interpels us from a political and from an ontological point of view.
From a queer transfeminist perspective, Nina Ferrante observes how the legacy of postmodernism in the 80s and the 90s, that of liquid and temporary identities, surrendered to the crystallization of practices, like glasses scattered in a kaleidoscope of given identities. Following an online protest of trans and drag-queens reclaiming the right to name their bodies, Facebook multiplied the choice in the drop-down menu under the gender box. But Facebook’s opening on issues such as gender binarism does not disrupt the identity paradigm. Instead, this new identity-based-design, starting from the data commons produced by Facebook users (the protest posts online) implemented a +1 logic which does not seriously question such a paradigm, neither from a political point of view nor from the point of view of data ecology. On the contrary, it becomes its proprietor and governs it.
On the basis of this kind of governance of practices crystallizing in identities, Tim Dean highlights the excess produced by occasions in their becoming properties. According to Dean, many people practicing sex without condom (like many monogamous gay couples) do not see themselves as being part of a bareback subculture, nor early porn from the ’70s were marketed as bareback porn. The subculture started its codification out of the massive campaign for prophylaxis in the wake of AIDS epidemics in the ’80s through the ’90s. In the same fashion, the biopolitical dispositif at the core of Grindr’s design (the cells and the tribes) individuates a set of physical, aesthetic, ethnic, cultural and medical data reducing them to bounded, properties and identities that cannot overlap (at least in its free version).
Properties and User Experience Design
To whom those properties belong, if by property we mean both attributes and possessions? Drawing on British philosopher and mathematician Alfred North Whitehead, Stamatia Portanova points out that a body’s properties are individuated through initial data, or occasions (that is the encounters or the practices); the work of individuations results in the production of data-commons that are readily made measurable and valued online. The capitalistic eco-logics of the app for sexual encounters catches the emerging properties of the bodies and harnesses them in the work of interaction with the app itself. Since a body’s attributes are also its possessions, the grid of Grindr’s interface transfers those assets into the sharing economy as information or data objects.
Not only are some data retained by the app as a privatized digital space but social relations themselves are fragmented and reduced to a one-to-one communication. Then they are made invisible to other users. An app for the commons, Portanova argues, would return the wealth of data to its “legitimate owners” but does not disrupt the functionalism embedded in the applicational ecologics, according to which the only point of access to an app is functionality (a capitalistic byproduct). In the case of Grindr, the function is the satisfaction of a sexual desire. Translated into the start-up lingo “there’s an app for that!”. And yet, the “dysfunctionalism” of hookup apps is what make them so irresistibly popular.
Talking to a friend about my research, we launched ourselves in an exercise of design fiction à la Black Mirror, by imagining apps allowing, as Uber and Airbnb do, the rating of the sexual performance of a partner/lover met online. This dystopian exercise made me reflect upon the necessity of imagining the app-to-come and upon the need to imagine it starting from a political view of the UX/UI Design. We do not know the scenarios opened by future technologies yet, but for the time being, the digital world is part of our experience of reality. What we can already do is to imagine the functions of the app-to-come – before the coming quantum phones scatter our categories of thought about binaries and amplitudes. And we can do it, by thinking about the occasion we want the app to produce: no longer single encounters but an ecology of relations, data of common properties designing a geography that can be safe and not secured, solidary and non-identitary.
It was late and I fell asleep with my phone on. While sleeping my quantified self was available for chatting, dating, getting bored together. The following morning I read the otter’s response to my message “I was in the mood for chatting but I fell asleep”. End of communications. A lost occasion?
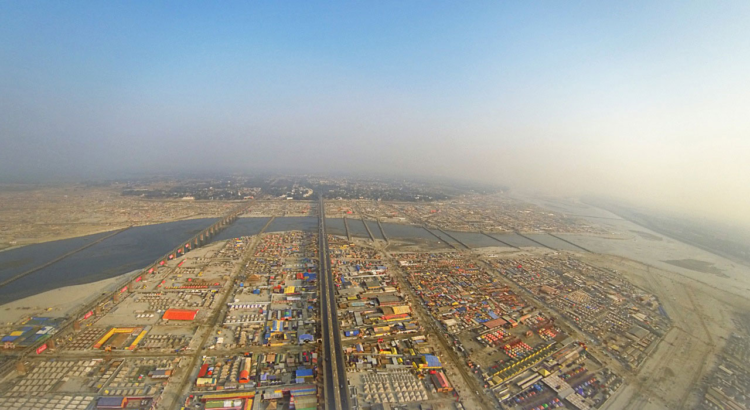

Città effimere e spazi condivisi: il modello Kumbh Mela a Venezia
In questi giorni abbiamo assistito al drammatico sgombero di Calais Jungle, il campo per rifugiati e immigrati, fermati alla frontiera tra Francia e Regno Unito. All’indomani della crisi siriana, la giungla ha visto la propria popolazione aumentare in modo sensibile, acuendo le drammatiche condizioni abitative, sanitarie e psicologiche che l’eterogenea popolazione viveva nel campo. Se l’attributo di giungla vuole sottolineare il forte contrasto tra l’assenza di regole all’interno del campo e il campo come espressione urbanistica del diritto internazionale, l’ultima delle tante giungle di Calais è stata sotto l’attenzione dei media anche per le forme di autorganizzazione di cui il campo si era dotato, con una toponomastica, ristoranti e drogherie, diventando così una città informale, persistentemente temporanea.
Le forme effimere di abitazione interrogano la Biennale di architettura di Venezia di quest’anno, il cui tema “Reporting from the Front” prende in considerazione le sfide contemporanee mettendo in questione lo stesso concetto di architettura. Lo apre cioè alla sua messa in discussione, alla rovina e all’effimero, a partire dallo studio dei materiali per arrivare alle metodologie di planning urbano, piegate dalle pressioni di una vita sempre più precaria e mobile.
Architettura come sintomo o come cura
Come mettere in contesti estremamente diversi le sfide proposte dall’abitare temporaneo in cui i luoghi di transito acquisiscono sempre più significati, e dove l’instabilità si inscrive come cifra stabile delle nostre vite? Come si identifica il limite se la moltiplicazione di frontiere produce il mondo-come-confine? L’intuizione del team curatoriale, guidato da Alejandro Aravena, è stata quella disseminare queste sfide in una rete di concetti, estremamente eterogenei tra loro, ma che costituiscono in fondo la missione dell’architettura: una continua ricerca estetica che rappresenti o che risponda al pensiero egemonico contemporaneo.
Qualità della vita, ineguaglianze, segregazione, insicurezza, periferie, migrazione, informalità, igiene, rifiuti, inquinamento, catastrofi naturali, sostenibilità, traffico, comunità, abitazione, mediocrità e banalità sono i 17 temi che strutturano la biennale di quest’anno. 17 temi che portano il peso delle loro criticità, ma è proprio il loro carattere ambivalente a interrogare gli studi e i team che hanno risposto alla call di Venezia. L’inflessione di queste tematiche raggiunge punte importanti quando si parla, come fa Making Heimat del padiglione tedesco, di coniugare il ripensamento della nazione con la concezione di arrival country; sia che si tratti di parlare di velocità di costruzione e smaltimento e di qualità dei materiali per garantire alle realtà urbane in veloce espansione di ripensarsi in modo rapido.
La conversione dell’antico Arsenale a spazio espositivo, ad esempio, fa il paio con il riutilizzo dei materiali di costruzione di questa edizione che provengono in gran parte da quelle precedenti. Attraversando questo spazio mi sono chiesto se l’architettura si limita a documentare e rappresentare la velocità del ciclo di produzione e distruzione, se si impegna a lenire il dolore provocato dalla crescente precarizzazione della vita oppure se al contrario si dedica all’opposizione di questo trend.
Governance nelle megacittà effimere

L’Arsenale, narrato attraverso planimetrie e modelli, viene interrotto dal progetto di ricerca di Rahul Merhotra e Felipe Vera della Harvard Graduate School of Design, Ephemeral Urbanism: Cities in constant flux. Il punto di partenza è Kumbh Mela, sulle rive del Gange: una città effimera di 23 chilometri quadrati che sorge in simbiosi con le cicliche piene del fiume in occasione dell’omonima festività religiosa. La più popolosa delle città temporanee è stata disegnata, montata, amministrata e smontata tra il 2012 e il 2014 (prima che il Gange si riprendesse la terra per renderla terreno agricolo fertile) e risorgerà nuovamente per il prossimo festival religioso che si terrà nel 2024.
Il punto più interessante della ricerca consiste nell’aspetto che riguarda il governo e la logistica della città nomadica, la stratificazione di soggetti statali e locali che gestiscono non solo la spazialità ma anche la temporalità della città. Ragionando con Kumbh Mela, Merhotra e Vera riflettono sull’urbanistica effimera che si attualizza secondo diverse modalità e scopi (rituali, celebrativi, emergenziali, di rifugio e di estrazione) come occasione per pensare a nuove forme di progettazione e management urbano che tengano presente l’accelerazione crescente del metabolismo delle metropoli e alle forme di identità culturali transitorie che in esse si realizzano.
Kumbh Mela rappresenta un’alternativa per pensare alla progettazione urbana in cui vari soggetti e soggettività collaborano per uno spazio condiviso, come alternativa alla gestione non partecipata di situazioni emergenziali, a quella spregiudicata di eventi globali come le Olimpiadi o i Campionati mondiali di Calcio e all’utopianesimo plutocratico di celebrazioni come il Burning Man che ha prodotto il modello Black Rock City, esportato in seguito sia in Israele che in Europa.
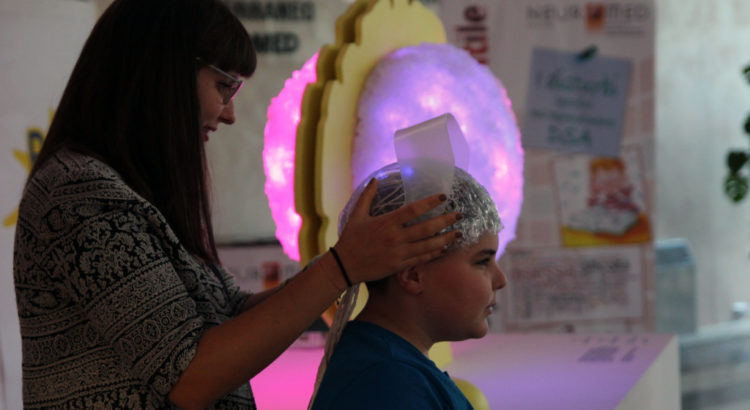
Baotaz: una protesi per dare un senso alla rete
Baotaz è un’istallazione artistica, un processo di creazione e condivisione di saperi, il prototipo di un senso prostetico che tenta di creare una nuova sensibilità, ovvero un abilità-a-sentire la realtà aumentata che sperimentiamo con i nostri corpi ogni volta che essi attraversano lo spazio digitale, producendo interazioni e dati online.
L’istallazione, progettata per la XXI Triennale di Design di Milano, è stata pensata e “fatta” durante La Cura Summer School a cui ho partecipato con grande interesse ed entusiasmo assieme ad altre quarantacinque persone provenienti dai più diversi ambiti, interessati all’interazione tra dati e corpi da diverse punti di vista (artistico, teorico, poetico, legale, del design e della ricerca)
I social media come ecosistemi
Human Ecosistems, il software aperto programmato da Salvatore Iaconesi, è stato lo strumento attraverso cui abbiamo “ascoltato” i social media come Instagram e Twitter rilevando le emozioni espresse dai post tramite un algoritmo di analisi del linguaggio naturale.

Durante la scuola abbiamo ad esempio visualizzato le relazioni tra gli utenti delle zone colpite dal terremoto di Amatrice, osservando l’emergere di una spazialità digitale complessa (ricca cioè di relazioni) laddove insisteva una richiesta di soccorso o una disponibilità a offrirlo. I dati processati da un computer sono stati tradotti in impulsi luminosi sul cervello in silicone (Baotaz Brain) e in vibrazioni sull’elmetto dotato di motorini (Baotaz Wearable) che reagiscono all’intensità dell’emozione e al livello di benessere espresso da ogni post.
La mente di chi? Tra individuale e sociale
Baotaz si trova ora nel parco tecnologico di Neuromed a Pozzilli (IS), dove dal 26 al 30 settembre è stato presentato ai ragazzi dei licei locali per la notte dei ricercatori. In questa occasione, abbiamo notato con grande sopresa che l’immaginario legato a un casco collegato a un computer è difficile da scalfire. Baotaz Wearable non legge infatti le emozioni di chi lo indossa, come molti – tra studenti ma soprattutto docenti credevano – ma decentralizza chi lo sperimenta in una rete che esprime non solo l’intelligenza sociale ma anche un affetto sociale.
Come sta il pianeta online oggi? Baotaz oltre a fornire una, non certo unica risposta, solleva più problemi di quanti ne risolva, circa ad esempio la questione della privacy e dello spazio pubblico digitale, privatizzato da piattaforme proprietarie che intercettano, catturano e mettono a valore i dati in rete.

Anglistica new issue: Inflections of Technoculture
Now online Anglistica AION’s new issue on Inflections of Technoculture. Biodigital Media, Postcolonial Theory and Feminism, edited by Iain Chambers e Tiziana Terranova.
This special issue of Anglistica aims at highlighting the blind spots between digital media properties and the questions posed by post-colonial subjects. Drawing on fields of inquiry as diverse as television and radio, cinema and cyberspace, new materialism and xenogenesis, the contributions help outline a composite theoretical framework trying to interrogate postcolonial ontologies and economies with regard to processes of inclusion/exclusion, the creation of borders, gendered and racial performance in a globalized world.
The contributors are mostly former doctoral students from the PhD program in Cultural and Postcolonial Studies at L’Orientale, and the Media and Communication department at Goldsmiths College, London, which makes this issue the result of an especially fruitful exchange between the two groups.
Inflection of Technocultures is available for free on Anglistica AION site.